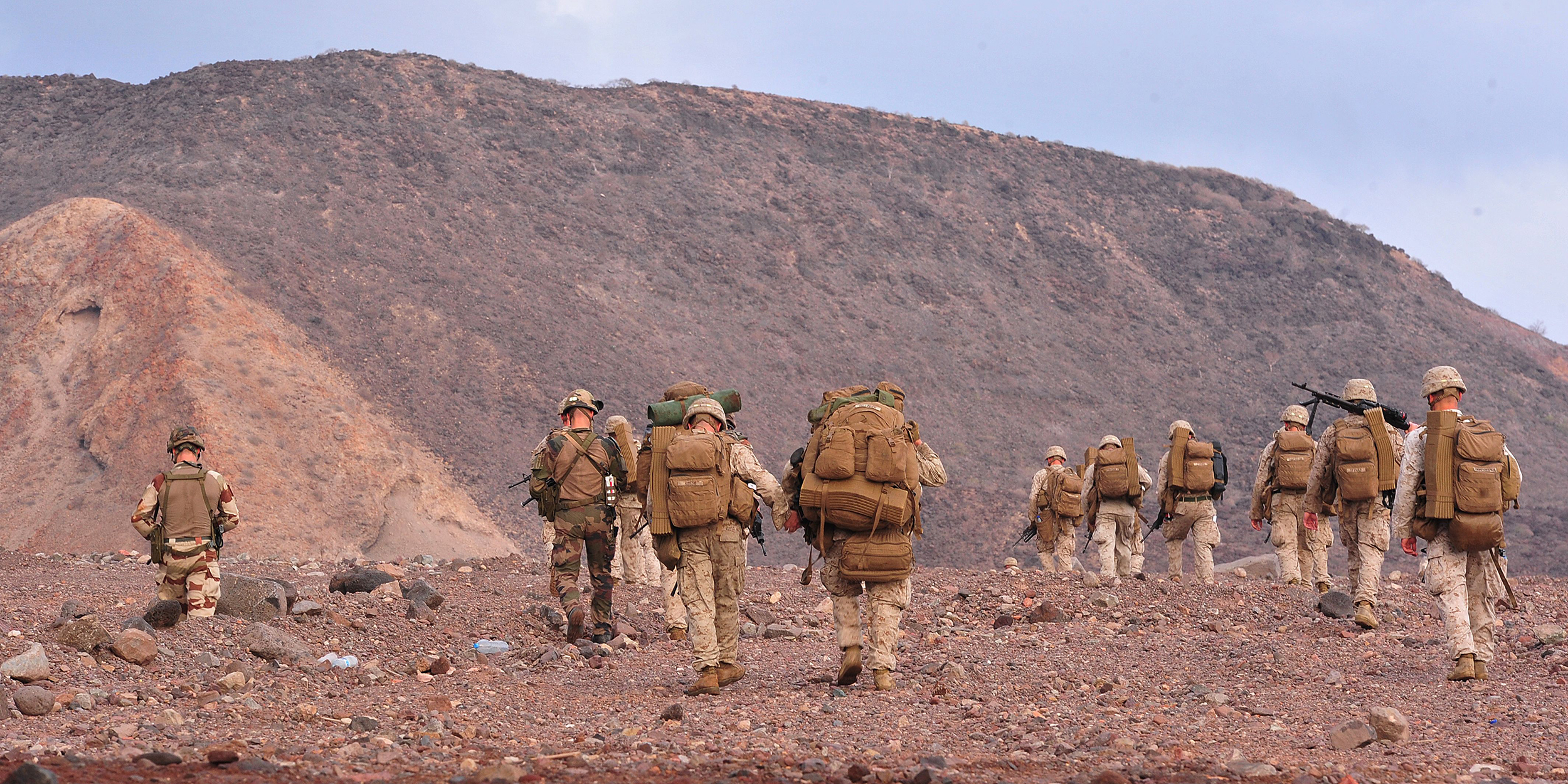
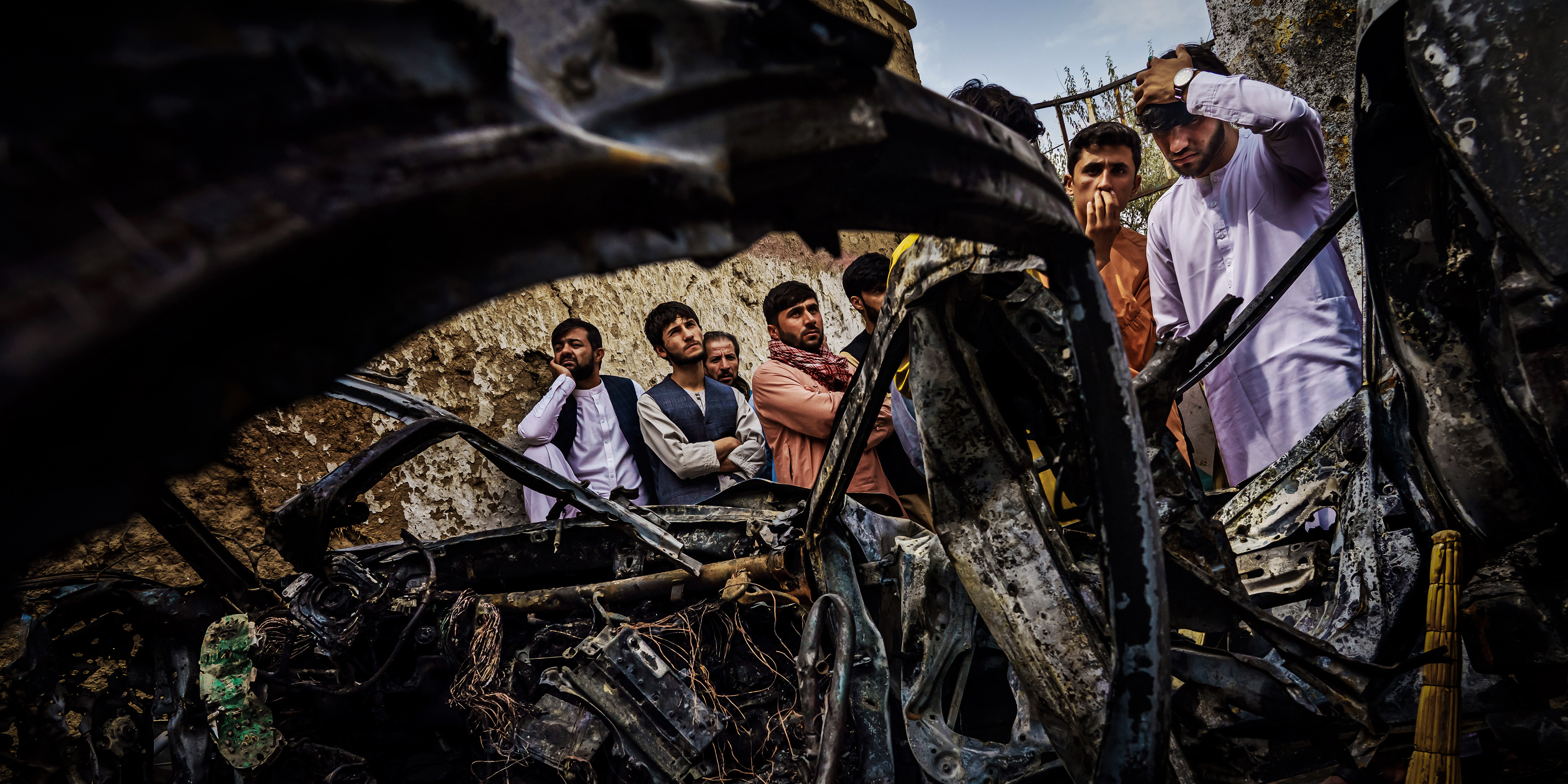The American military has been carrying out a continuous military campaign in Somalia since the 2000s, launching nearly 300 drone strikes and commando raids over the past 17 years.
In one April 2018 air attack, American troops killed three, and possibly five, civilians with a pair of missiles. A woman and child were among the dead, according to a U.S. military investigation, but the same report concluded their identities might never be known.
Last year, my investigation for The Intercept exposed the details of this disastrous attack. The woman and child survived the initial strike but were killed by the second missile. They were 22-year-old Luul Dahir Mohamed and her 4-year-old daughter, Mariam Shilow Muse.
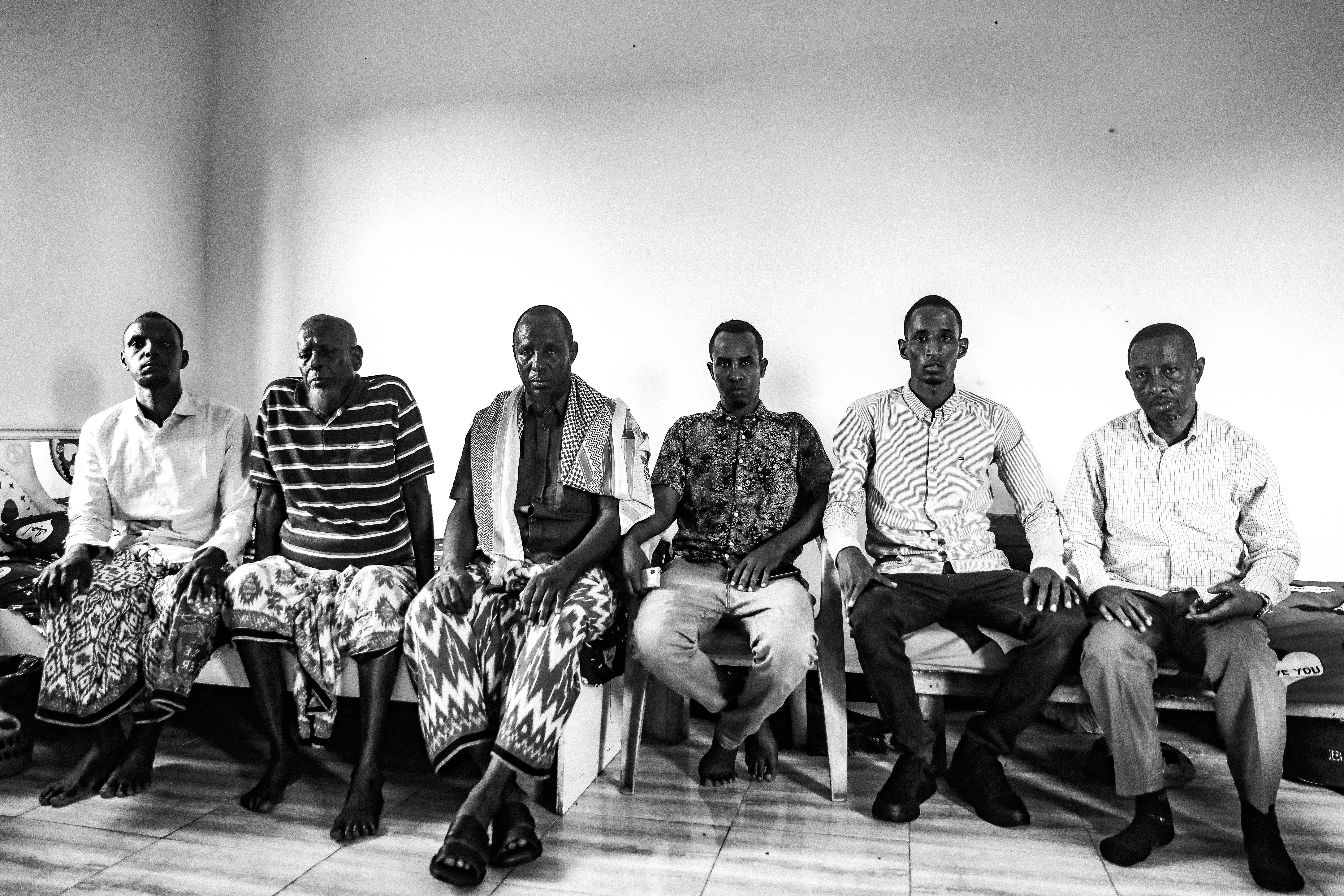
For six years, the family has tried to contact the U.S. government, including through an online civilian casualty reporting portal run by U.S. Africa Command, or AFRICOM, but they have never received a response. “They know innocent people were killed, but they’ve never told us a reason or apologized,” Abdi Dahir Mohamed, one of Luul’s brothers, told me last year. “No one has been held accountable.”
A new report by the Center for Civilians in Conflict, or CIVIC, shared exclusively with The Intercept, underlines what Mohamed told me: Civilian victims and survivors of U.S. drone strikes in Somalia say that attaining justice in the form of official acknowledgment, apologies, and financial compensation would help them move on from the trauma they experienced.
But after almost 20 years of drone strikes, even in cases in which the Pentagon has admitted to killing innocent people, the U.S. has failed to apologize to any Somali survivors, much less offer amends.
“The civilians we interviewed described not only devastating physical harm, like deaths and injuries, but also significant economic burdens and long-lasting psychological trauma,” Madison Hunke, CIVIC’s U.S. program officer, told The Intercept. “Most respondents agreed that justice comes down to a perpetrator of harm being held accountable for their actions and the victims being treated with the dignity they deserve.”
CIVIC interviewed 38 individuals who identified as civilian victims of U.S. airstrikes in Somalia, as well as eight civil society experts who work with or represent the injured and survivors. Twenty-seven of the 38 lost a family member in an attack. Many spoke of justice in terms of U.S. accountability, including acknowledgment of the deaths, apologies, and financial amends, specifically a Somali custom known as diya (blood money) which is traditionally used to resolve disputes.
“For me, justice would mean the U.S. talking and sitting with the families of the civilian victims harmed in its airstrikes,” one interviewee told CIVIC. “Then the U.S. should financially compensate those families. That kind of move would eventually heal the wounded hearts.”
After more than 17 years of drone strikes and ground attacks in Somalia, the U.S. has carried out 288 declared strikes. AFRICOM claims to have killed just five civilians in that period, including Luul and Mariam. (The military has never referred to the mother and daughter by name.) Airwars, the U.K.-based airstrike monitoring group, says the real number may be more than 3,000 percent higher.
Following The Intercept investigation last year, two dozen human rights organizations — 14 Somali and 10 international groups — called on Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin to compensate Luul and Mariam’s family. This year, Sen. Elizabeth Warren, D-Mass., and Reps. Sara Jacobs, D-Calif.; Ilhan Omar, D-Minn; Barbara Lee, D-Calif.; and Jim McGovern, D-Mass., joined the effort.
“The Department of Defense is currently reviewing this matter, and we will not comment further at this time,” Pentagon spokesperson Lisa Lawrence said of the case.
The Defense Department’s response has compounded the trauma suffered by survivors, says Clare Brown, the deputy director of Victim Advocates International, an organization that supports victims of international crimes that is representing the families of Somali drone strike victims, including Luul’s.
“The silence of AFRICOM and the U.S. Department of Defense towards the families has been really hurtful,” Brown told The Intercept. “As their lawyers, we know that there are discussions and even possibly some movement happening behind the scenes — but no one has reached out or spoken to the families.” Brown and other lawyers are the families’ only source of information. “It’s upsetting for them to feel like passive observers in this process they are actually at the center of,” Brown said.
The forms of harm chronicled in the CIVIC report include the death of a relative, physical injury, property damage, and economic hardship experienced by victims and survivors of U.S. drone strikes.
Fourteen interviewees reported that they or family members experienced ongoing psychological trauma because of the attacks. “A considerable amount of time has elapsed since the incident, but I still experience nightmares,” one man whose sister was killed in a strike told CIVIC. “The incident and the gruesome details of what happened to her deeply affect me.”
CIVIC’s research found that a majority of civilian victims and survivors indicated a preference for individual amends like condolence payments or financial assistance over community-level compensation, such as improving local infrastructure. “The report is a good reminder that we can’t know what justice means to people unless we ask them,” said Brown. “The U.S. should also be proactively trying to have these conversations with communities affected by drone strikes — and hopefully this report will create the impetus for them to find ways to do that.”
CIVIC’s report includes 11 recommendations for the U.S. government, including adoption of a comprehensive approach to accountability and amends, prioritization of individual amends to victims and survivors of attacks, and the utilization of $3 million authorized annually by Congress for ex gratia payments to victims and survivors of civilian harm.
In April, one year past its congressionally-mandated deadline, the Pentagon released its 2022 annual report on civilian casualties. It concluded that U.S. military operations in 2022 killed no civilians, and also noted that the Defense Department did not make any ex gratia payments to civilians harmed in its operations in 2022 or the families of those killed in strikes from previous years. This follows a single ex gratia payment made in 2021 and none issued in 2020.
It’s impossible to know if any payments to survivors were made last year because the Defense Department missed its May 1 deadline for releasing its 2023 civilian casualty report. Lawrence told The Intercept that the Pentagon is still reviewing data and expected the overdue report to be released “in the near term.”
In the meantime, Somali survivors continue to wait, wondering if the Pentagon will ever apologize for killing their relatives.
“Since 2020, when Congress first authorized the $3 million annually for ex gratia, the Department has reported just one single payment of just a few thousand dollars has been made, and that’s despite the many credible cases of harm the DoD has already publicly acknowledged,” CIVIC’s Hunke told The Intercept. “The U.S. has the tools it needs to make these payments, so it’s a question of political will.”
“The lack of payments in Somalia, as well as in other places like Iraq and Syria, speaks volumes about the DoD’s commitment to meaningfully respond to harm caused by its operations,” Hunke said.
Latest Stories

AIPAC Millions Take Down Second Squad Member Cori Bush
Bush was early calling for a ceasefire in Israel's war on Gaza. Then AIPAC came after her with millions of dollars.

The U.S. Has Dozens of Secret Bases Across the Middle East. They Keep Getting Attacked.
An Intercept investigation found 63 U.S. bases, garrisons, and shared facilities in the region. U.S. troops are “sitting ducks,” according to one expert.

What Tim Walz Could Mean For Kamala Harris’s Stance on Gaza and Israel
Walz allows for Harris to “turn a corner” in her policy on the war in Gaza, said James Zogby, president of Arab American Institute.